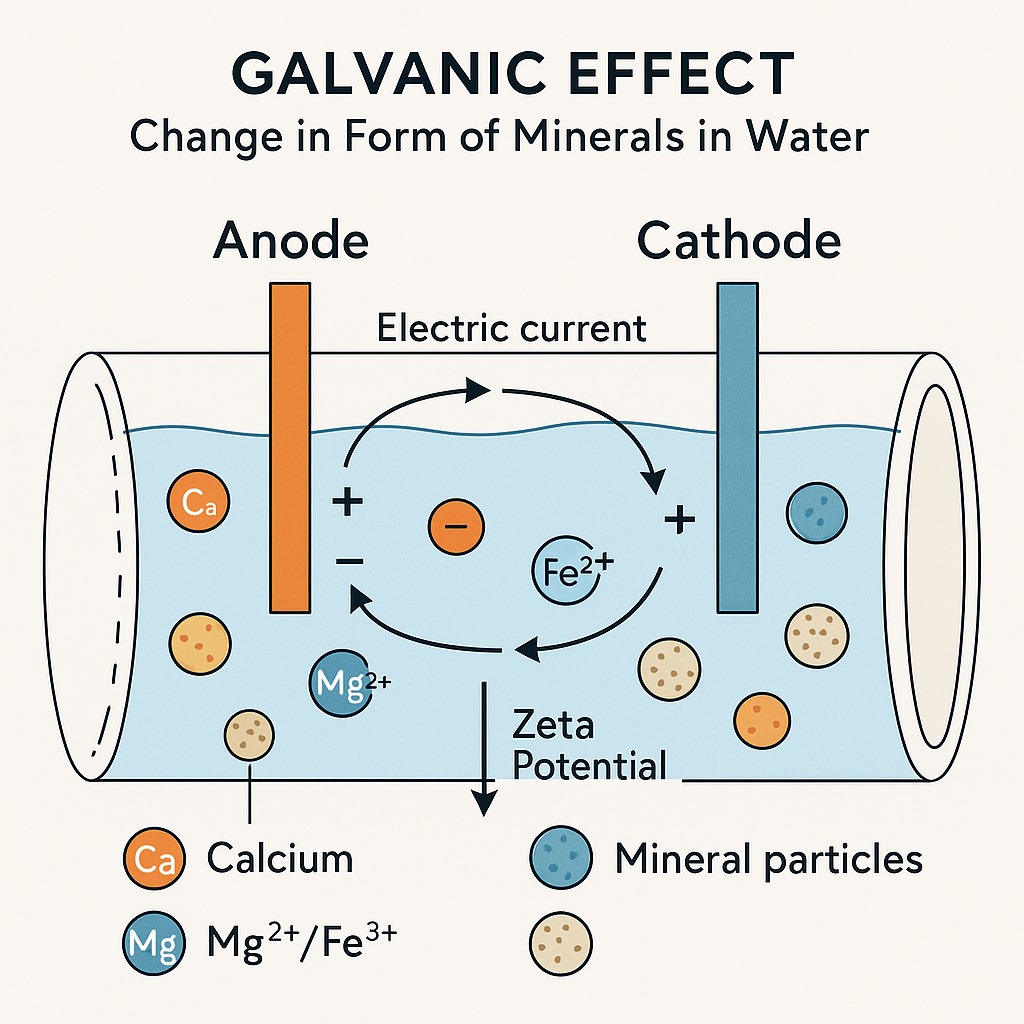
When two different metals (like #zinc and #copper) are in contact inside water, they cause a galvanic reaction — like a mini battery.
This reaction produces a tiny electric field in the water flowing around the metal core.
💧 2. Minerals in Water (like #Calcium and #Magnesium)
In #HardWater, minerals like calcium (Ca²⁺) and magnesium (Mg²⁺) usually float around as positively charged particles.
These particles tend to cluster together and stick to surfaces, causing scale on pipes, pumps, and tanks.
🔄 3. Electric Field Affects Their “#ZetaPotential”
Here’s where zeta potential comes in:
👉 Zeta potential is like an “electric shield” around each tiny particle.
It controls whether particles stick together or stay apart in the water.
👉 When the galvanic effect happens:
The tiny electric field alters the zeta potential of mineral particles.
It gives them a stronger electrical “push” away from each other.
So instead of clumping and forming scale, they stay apart, suspended in water.
🧼 4. Result: Softer Behavior Without Removing Minerals
The minerals are still there — but in a different form.
They may become tiny crystal-like shapes or soft powder that doesn’t stick to surfaces.
This makes water act like #softwater without using salt or chemicals.
🧪 Summary in One Line:
The galvanic effect changes the surface charge (zeta potential) of minerals, so they stop clumping and scaling — they float freely instead of sticking.
Check out 👉 https://igswater.com/products/water-conditioners/ at IGS WATER

